
by John Walt Childers, IPC-CID, Founder of Golden Gate Graphics
Formerly known as
This glossary has key terminology in use in PCB design and manufacturing, with a smattering of electronics. The definitions were chosen so that their context would likely apply to reading material encountered by a PCB designer. Therefore, many of these terms will have other meanings not given here. See recommended dictionaries below.
This collection of terms came about as I, a PCB designer, ran across words and acronyms in my field for which meanings were hard to find. As I tracked them down, I made them part of this glossary. If you are a PCB designer, then this glossary could be a good place to start when you find a need to look up the meanings of words related to printed circuits or electronics.
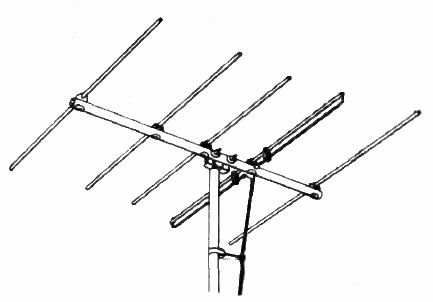
Yagi antenna — (YAH-gee an-TEN-uh) Pronunciation Key noun [RF Engineering]
A Yagi antenna is a directional antenna consisting of multiple parallel elements in a line, usually half-wave dipoles made of metal rods. The functional elements of this directional antenna consist of a driven element (aka signal, one or more passive directors, and a reflector, arranged in a linear fashion along a boom. It is widely used in radio frequency (RF) communications for applications such as television reception, amateur radio, and wireless networking due to its high signal gain and focused signal directivity.
The Yagi antenna exists because of the need for enhanced signal directionality and gain in RF communications. By utilizing parasitic elements, the antenna improves reception and transmission efficiency, allowing signals to be sent and received over longer distances while minimizing interference from unwanted directions.
The primary effects of a Yagi antenna include improved strength in a specific direction, increased communication range, and reduced interference from signals coming from undesired directions. It is commonly employed in broadcasting, satellite tracking, and point-to-point communication systems.
A Yagi antenna's performance can be altered by adjusting the number, length, and spacing of its elements, which impact gain, bandwidth, and directivity. It can also be fine-tuned by modifying the placement of the reflector and directors to optimize performance for a specific frequency range.
The Yagi antenna was invented by Japanese engineers Shintaro Uda and Hidetsugu Yagi in the 1920s. It is often referred to as a "Yagi-Uda antenna," recognizing both contributors. The design became widely known after Yagi introduced it to the Western world, leading to its widespread adoption in radio and television technology.
Terms that begin with a symbol or a digit are placed in the SYMBOLS page. Terms that contain digits within them are alphabetized as if the numeric
characters were spelled in English.
Terms with two or more words are alphabetized "dictionary style." They are alphabetized as though the spaces between the terms have been removed.
If there are other characters in the term, such as a slash (/), dash (-) or plus sign (+), these are treated the same as spaces and ignored for the purpose of alphabetizing.
This is the best, most usable dictionary for electronics, because its
definitions help you grasp the terms and therefore the subject. Lesser
dictionaries define electronics terms with even more difficult technical
jargon, leading one into endless"word chains." Not this one.
You can
buy the Modern Dictionary of Electronics new or used
via the Internet.
You need a big, comprehensive dictionary. Get this one. Despite being a big dictionary, The Random House has great definitions, quick to grasp.
Although out of print, as of 2022 you could still buy a great used copy online for $40 including shipping or possibly for much less. Two versions are available of the 2nd Edition, Unabridged:
